Cavernous sinuses of brain 178591-Is the cavernous sinus part of the brain
One anterior and the other posterior to the infundibulum They drain posteriorly by the petrosal sinuses Petrosal sinuses Superior petrosal · The cavernous sinus is a centrally located cavity situated at the base of the brain next to the temporal bone and sphenoid bone Its Latin name is sinus cavernosusCavernous malformations are clusters of abnormal, tiny blood vessels and larger, stretchedout, thinwalled blood vessels filled with blood and located in the brain These blood vessel malformations can also occur in the spinal cord, the covering of the brain (dura) or

Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Emcrit Project
Is the cavernous sinus part of the brain
Is the cavernous sinus part of the brain-Case Discussion It is not uncommon for small deposits of fat to exist intracranially within the falx and around the cavernous sinuses With standard CT brain window settings these fat deposits appear black and can be misinterpreted as being air (pneumocephalus) byThis video covers the anatomy of the cavernous sinus (lateral sellar compartment), its location, drainage and function Test yourself on the dural venous sin



Cavernous Sinus Neuroangio Org
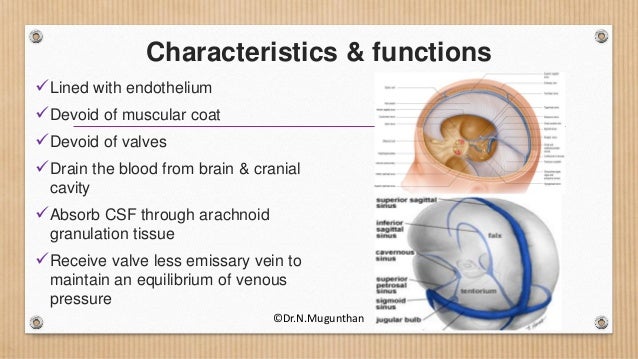
Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) occurs when a blood clot forms in the brain's venous sinuses This prevents blood from draining out of the brain As a result, blood cells may break and leak blood into the brain tissues, forming a hemorrhage This chain of events is part of a stroke that can occur in adults and children · Symptoms of cavernous sinus thrombosis may include Severe headache often accompanied by tearing Swelling, redness, or irritation around one or both eyes Drooping eyelids Inability to move the eye High fever Pain or numbness around the face or eyes Fatigue Vision loss or double vision Seizures · The cavernous sinus is a paired dural venous sinus located within the cranial cavity It is divided by septa into small 'caves' from which it gets its name Each cavernous sinus has a close anatomical relationship with several key structures in the head
· The cavernous sinus is the only one of the paired dural sinuses that communicates with each other These sinuses have two intercavernous branches arching over the diaphragma sellae of the pituitary gland;The cavernous sinus is the only one of the paired dural sinuses that communicates with each other These sinuses have two intercavernous branches arching over the diaphragma sellae of the pituitary gland; · FIGURE 732 Three patients with developmental cysts involving the cavernous sinus A–C Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) study in Patient 1 In (A), the contrastenhanced T1weighted (T1W) image shows a cystic mass involving the cavernous sinus (arrow)In (B), the coronal image confirms the location of the cyst (arrow) and compression of the trigeminal cistern
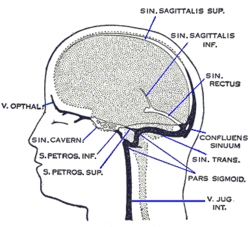
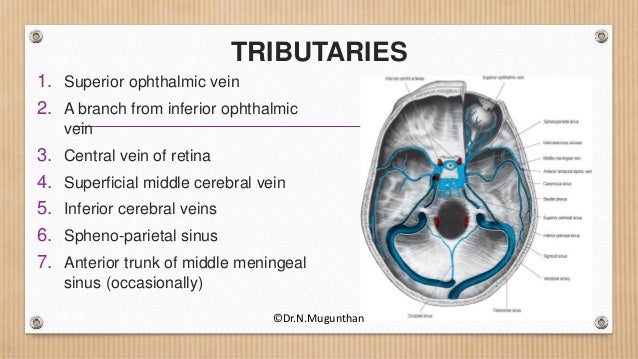
One anterior and the other posterior to the infundibulum They drain posteriorly by the petrosal sinuses · The cavernous sinuses receive venous blood from the facial veins (via the superior and inferior ophthalmic veins) as well as the sphenoid and · The cavernous sinus thrombosis is an infection leading to blood clot caused by the complication of an infection in the paranasal or central face sinuses Advertisement The infection may obstruct the blood flow from the brain due to the complicated neurovascular relationship




Schematic Drawing Of The Basal Cerebral Venous Drainage Routes Download Scientific Diagram




Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Circulation
A cavernous sinus meningioma is a benign tumor arising from the cells that form the internal lining membrane of the brain, called the pia mater, which expands to fill the cavernous sinus The cavernous sinus has many vital structures passing through it, including the carotid artery and the third, fourth, fifth, and sixth cranial nervesInferior petrosal sinus=light blue; · Cavernous sinus meningiomas – benign yet threatening tumors – are lodged in a most inconvenient location They sit above the skull at the base of the brain, surrounded by no fewer than five cranial nerves and the internal carotid artery



The Cavernous Sinus Contents Borders Thrombosis Teachmeanatomy




Cavernous Sinus Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Cavernous sinus thrombosis (CST) is the formation of a blood clot within the cavernous sinus, a cavity at the base of the brain which drains deoxygenated blood from the brain back to the heartThis is a rare disorder and can be of two types–septic cavernous thrombosis and aseptic cavernous thrombosis Most commonly the form is of septic cavernous sinus thrombosis · Each of the paired cavernous sinuses is a venous lake situated lateral to the sella turcica, the pituitary gland, and the sphenoid sinus and medial to the medial aspect of the temporal lobe of the brain The term cavernous sinus was first used by Winslow in 1734 owing to the multiple filaments, or septa, within, which gave it a cavernous or plexiform appearance However, thisCavernous sinus an irregularly shaped venous channel between the layers of dura mater of the brain, one on either side of the body of the sphenoid bone and communicating across the midline Several cranial nerves course through this sinus cerebral sinus one of the ventricles of the brain



Cavernous Sinus Wikipedia



Dural Venous Sinuses Cavernous Sinus Dr N Mugunthan
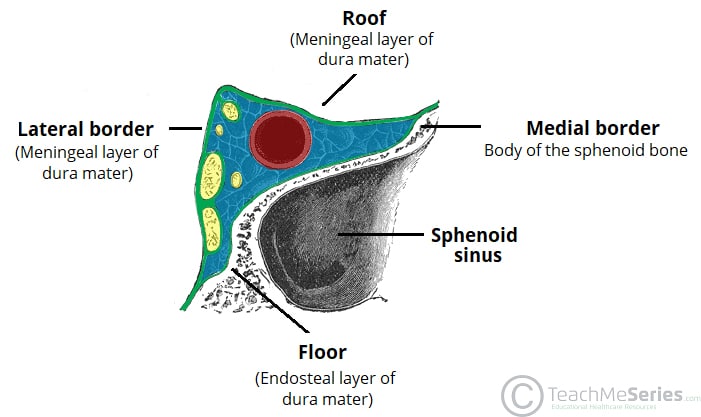
Cavernous sinuses drain the blood from the orbits through the ophthalmic veins and from the anterior part of the base of the brain by the sphenoparietal sinus and the middle cerebral veins They empty into both the superior and inferior petrosal sinuses and · Cavernous sinus cavernoma is a rare vascular malformation, which represents 3% of all benign cavernous sinus tumors 1 Marked hyperintensity on T2weighted images with intense and homogenous enhancement are characteristic Red cell–labeled blood pool scintigram is more specific for diagnosis 2The cavernous sinus is located on either side of the pituitary fossa and body of the sphenoid bone between the endosteal and meningeal layers of the dura It spans from the apex of the orbit to the apex of the petrous temporal bone Unlike other dural venous sinuses, it is divided by numerous fibrous septa into a series of small caves, which is



Dural Venous Sinuses Cavernous Sinus Dr N Mugunthan




38 The Cavernous Sinus Cavernous Applied Anatomy Study Facebook
· Septic thrombosis of the cavernous sinuses (or cavernous sinus thrombophlebitis CST) is a dramatic and potentially lethal illness, which is still occasionally seen by clinicians Before the availability of antimicrobial agents, mortality from CST was near 100%, but it · Cavernous sinus anatomy 1 Cavernous Sinus ByDr Noura El Tahawy 2 Position & Extensionon the side of the body of sphenoid,extending from the apex of the petrous temporal bone (behind)to the medial end of the superior orbital fissure (in front)Each sinus is 2 cm long and 1 cm wide, 3 Relations 4The cavernous sinus (Figs 759–761), one on each side, situated on the body of the sphenoid bone, extends from the superior orbital fissure to the apex of the petrous temporal bone Medially, the cavernous sinus is related to the pituitary gland and the sphenoid sinus Laterally, it is related to the temporal lobe of the brain




Dural Venous Sinuses Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org




Reflecting On Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis And The U S Presidential Election The Stroke Blog
The cavernous sinuses The cavernous sinuses are a series of hollow spaces located under the bottom of the brain, behind each eye socket Each forms a major vein that is part of a network of sinuses that eventually drain into the jugular veins, which carry blood away from the brainThe dural sinuses about the base of the skull have received little attention in radiological literature When opacified, the cavernous sinus together with the intercavernous sinuses offer intimate information about the configuration of the pituitary glandDominance of one transverse sinus over another is routine Cavernous sinuses are usually symmetric in their development — spectrum from very large to essenially absent Except when they are asymmetric Rare but still normal




Venous Drainage Of The Brain And The Dural Venous Sinuses Dural Venous Sinuses Anatomy
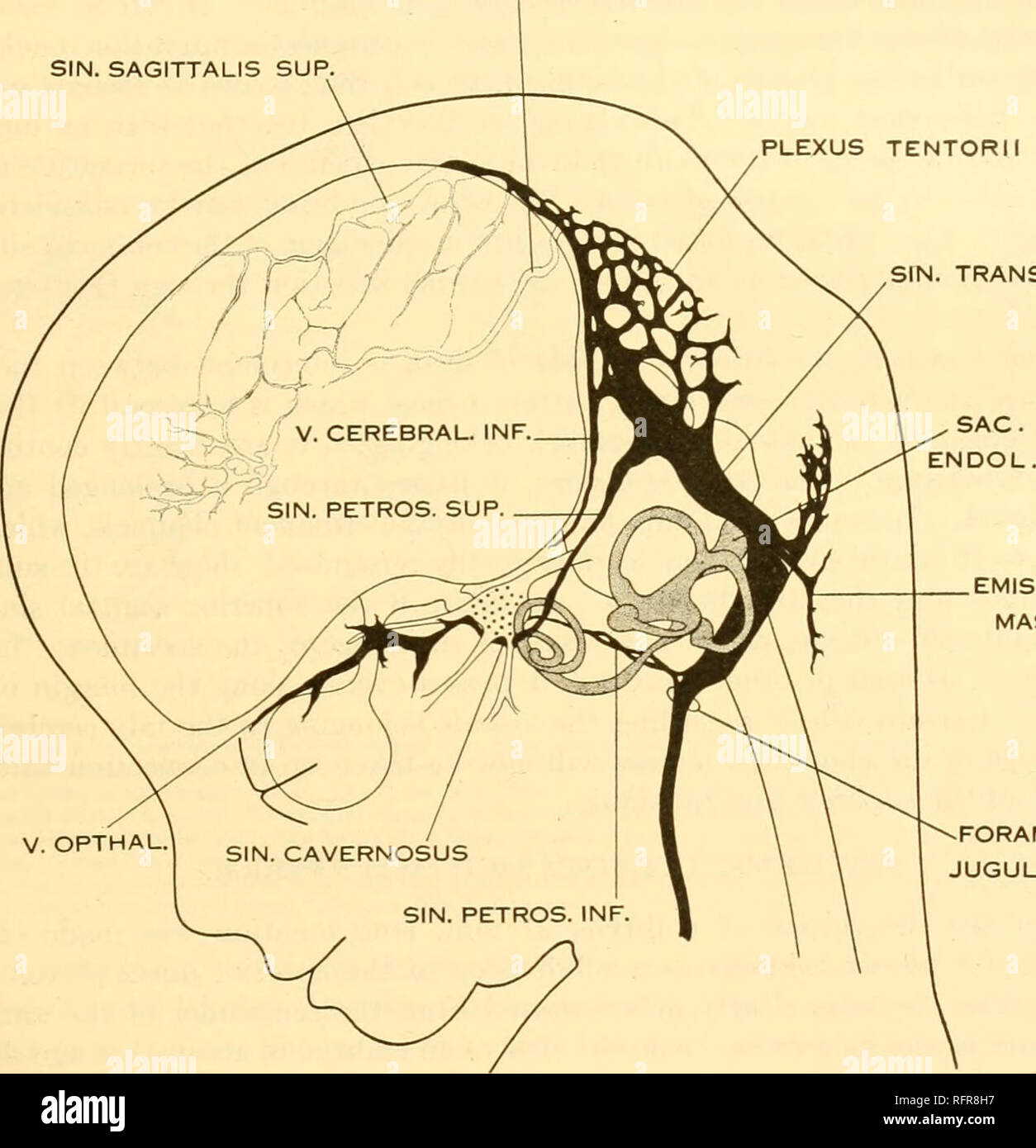



Carnegie Institution Of Washington Publication Of The Brain Of The Human Embryo 29 The Large Ophthalmic And Maxillary Tributaries In Front In Figure 27 It Receives A Large Terminal Trunk Lateral
· The tumor removal of Cavernous Sinus Meningiomas usually results in severe neurological deficits Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) and fractionated Stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT) are advanced modalities of radiotherapy for treatment of patients with inoperable and symptomatic CSMs The authors evaluated the long term symptomatology, the image findings, · Indirect CCFs form between the cavernous sinus veins and branches of the carotid artery in the membranes that enclose your brain The rate of blood flow in these fistulas is usually low Symptoms · Aneurysm is a reflex of arterial dilatation that results in weakening of the arterial wall 5 It can be sacculate, fusiform or dissecting, being possible in any intracranial location 5 Aneurysms in the cavernous segment of the internal carotid artery account for 2% to 9% of all intracranial aneurysms and are completely extradural and present a risk of developing




Dural Venous Sinuses 3d Anatomy Tutorial Youtube
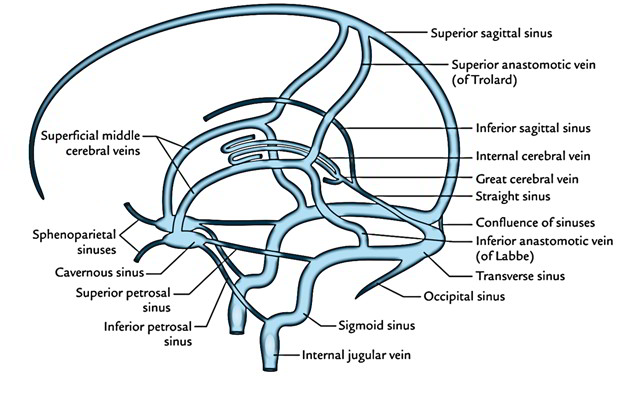



Dural Venous Sinuses
· A cavernous hemangioma is a collection of abnormal, dilated blood vessels in the brain A cavernous hemangioma may also be known as a cavernoma, a 'cavmal', a cavernous angioma, or a cerebral cavernous malformation All these terms are equivalent, meaning they describe the exact same thingSign up now on our website at https//wwwDrNajeebLecturescom to access 800 Exclusive videos on Basic Medical Sciences & Clinical Medicine · Cavernous sinus Structure The cavernous sinuses are 1 cm wide cavities that extend a distance of 2 cm from the most posterior aspect of Contents The cavernous sinus contains the internal carotid artery and several cranial nerves Abducens nerve (CN VI) Relations There are numerous




Cavernous Sinuses Neurology Medbullets Step 1



Cavernous Sinus Neuroangio Org
· The straight sinus is a continuation of the great cerebral vein and the inferior sagittal sinus From the confluence, the transverse sinus continues bilaterally and curves into the sigmoid sinus to meet the opening of the internal jugular vein The cavernous sinusThe purpose of this article was to review the anatomy of the cavernous sinus (CS), illustrate numerous lesions that can affect the CS, and emphasize the imaging characteristics for each lesion to further refine the differential diagnoses The CS, notwithstanding its small size, contains aSigmoid sinus=purple The inferior sagittal sinus is highly variable in extent of development and course This one (light blue) has an unusual craniocaudal orientation Notice complete lack of cavernous sinus capture by the sylvian veins, which drain instead towards the sigmoid region




Dural Venous Sinuses An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
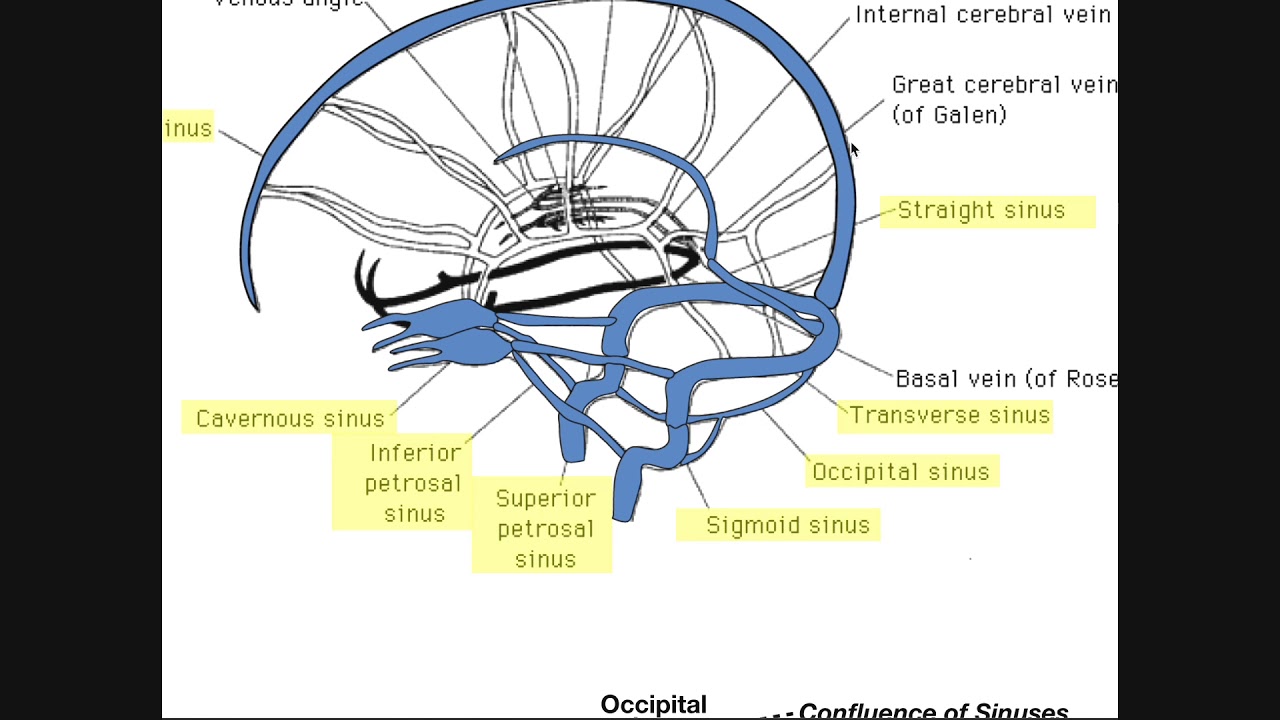



Cranial Sinuses Anatomy Ordered Flow Of Venous Blood Youtube
Cavernous sinus in a patient with decreased mental status and a right subclavian line The contrast scan after this noncontrast scan showed no change in the cavernous sinus gas unlikely to be in or around the nerves, connective tissue, or fat that fills the nonvascular portions of the cavernous sinus99 · Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) of the cavernous sinus are abnormal communications between the dural branches of the internal, or external carotid arteries, or both, and the cavernous sinus These abnormalities can cause chemosis, proptosis, and bruit (1) and, rarely, infarction or hemorrhageThe cavernous sinuses are hollow spaces located under the brain, behind each eye socket A major blood vessel called the jugular vein carries blood through the cavernous sinuses away from the brain A blood clot can develop when an infection in the
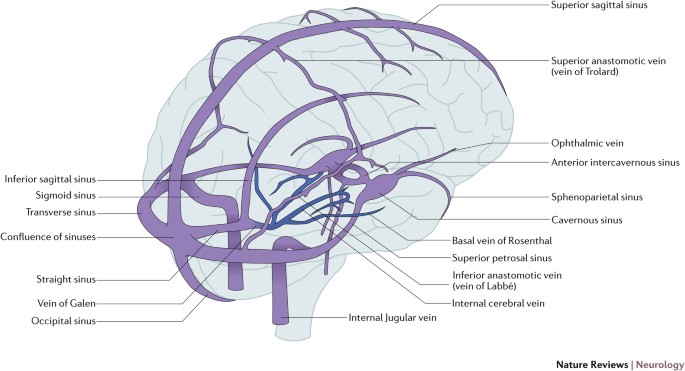



Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Nature Reviews Neurology
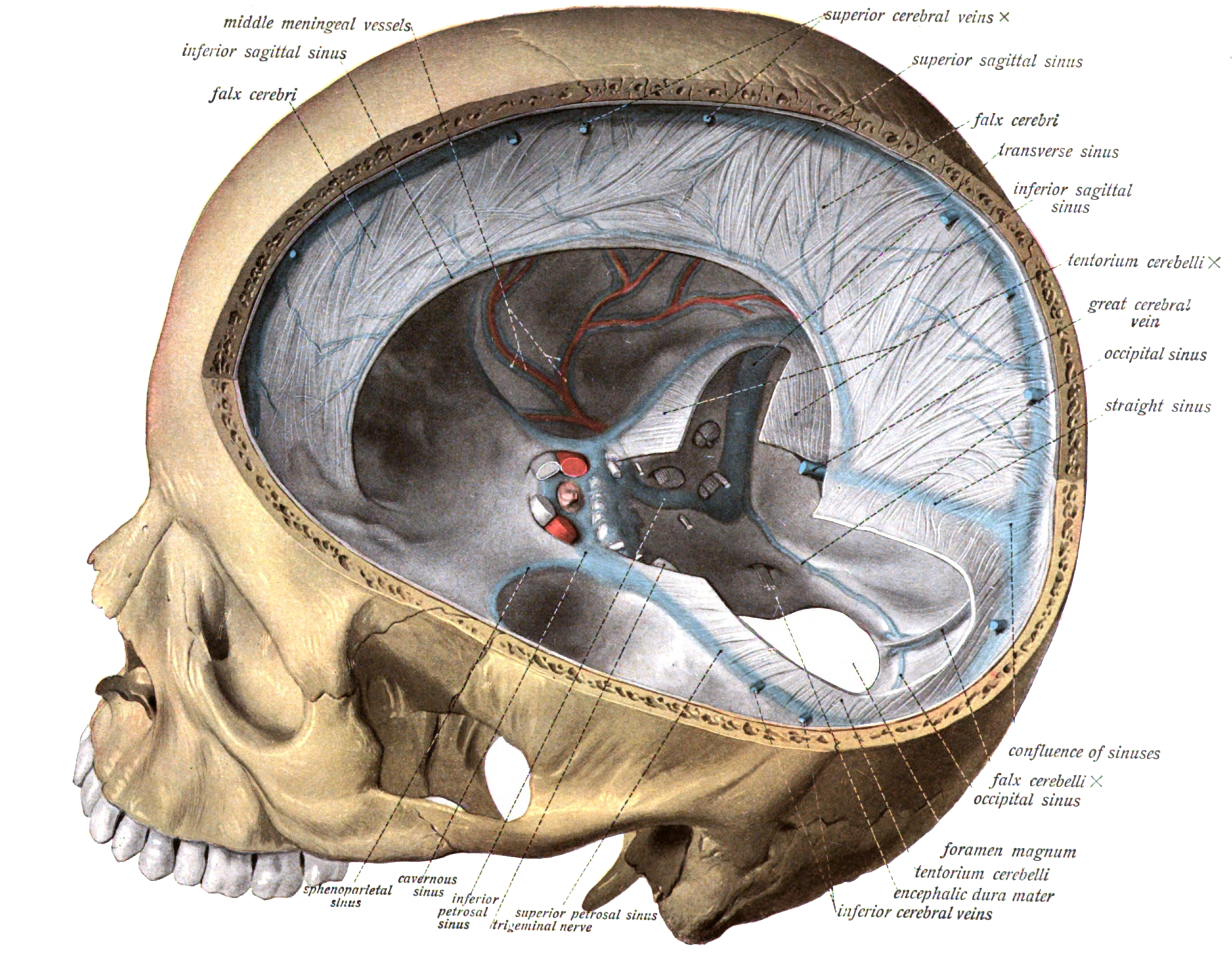



Dural Venous Sinuses Wikipedia
· The cavernous sinus (CS) pair is located near the center of the head on each side of the sella and body of the sphenoid bone Each sinus has dural walls that surround a venous space through which a segment of the carotid artery with its branches, the abducens nerve and the sympathetic plexus, courseBackground Meningiomas are the most common tumor involving the cavernous sinus Although these tumors have been known to invade adjacent structures such as bone, soft tissue, and brain, invasion of the internal carotid artery (ICA) by meningiomas has only been recognized recently · The cavernous sinuses are hollow spaces located at the base of your brain and behind your eye sockets They allow major veins to drain blood from your brain and face The blood clot typically forms




Cavernous Sinus Location And Relations Tributaries Connections Thrombosis Anatomyqa
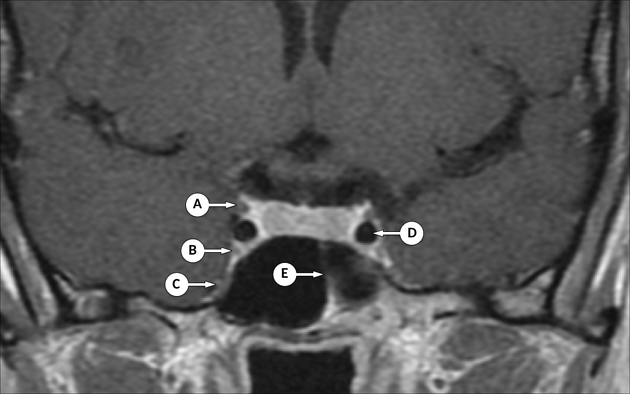



Cavernous Sinus Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
The cavernous sinus receives blood from veins of the face and brain The blood drains it into other blood vessels that carry it back to the heart This area also contains nerves that control vision and eye movements Cavernous sinus thrombosis is most often caused by a bacterial infection that has spread from the sinuses, teeth, ears, eyes
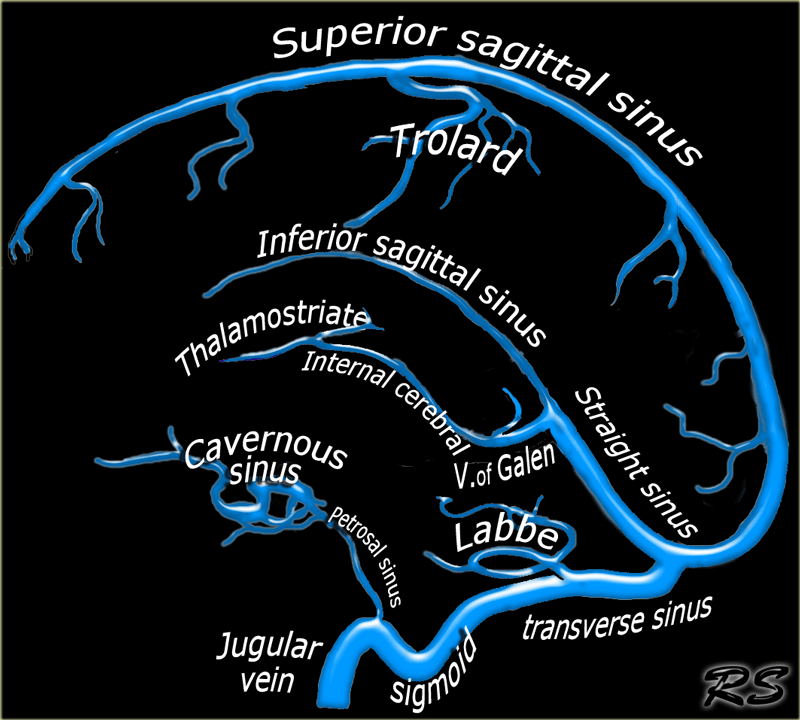



The Radiology Assistant Cerebral Venous Thrombosis




Cavernous Sinus Draw It To Know It Neuroanatomy Youtube
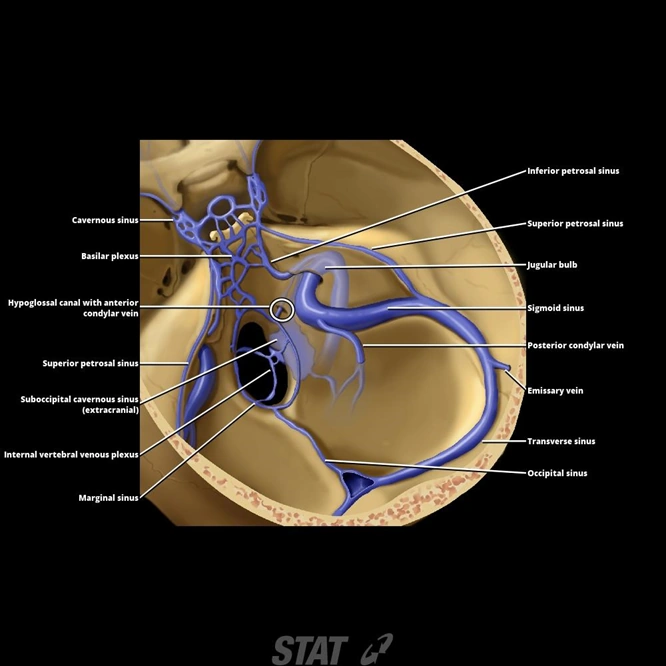



Venous Supply To Brain Venous Sinuses Ranzcrpart1 Wiki Fandom
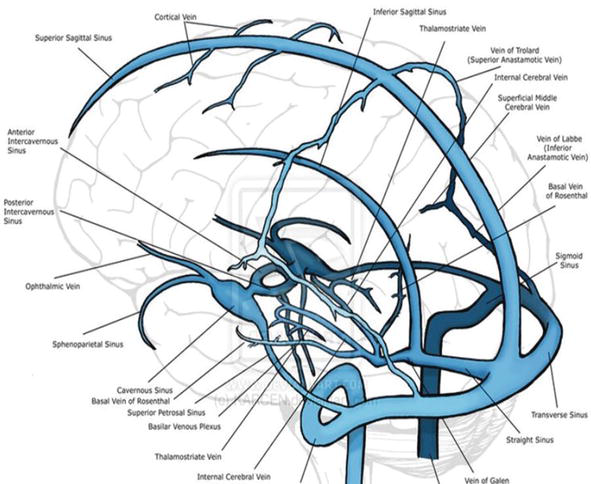



Cerebral Vein And Dural Sinus Thrombosis Intechopen
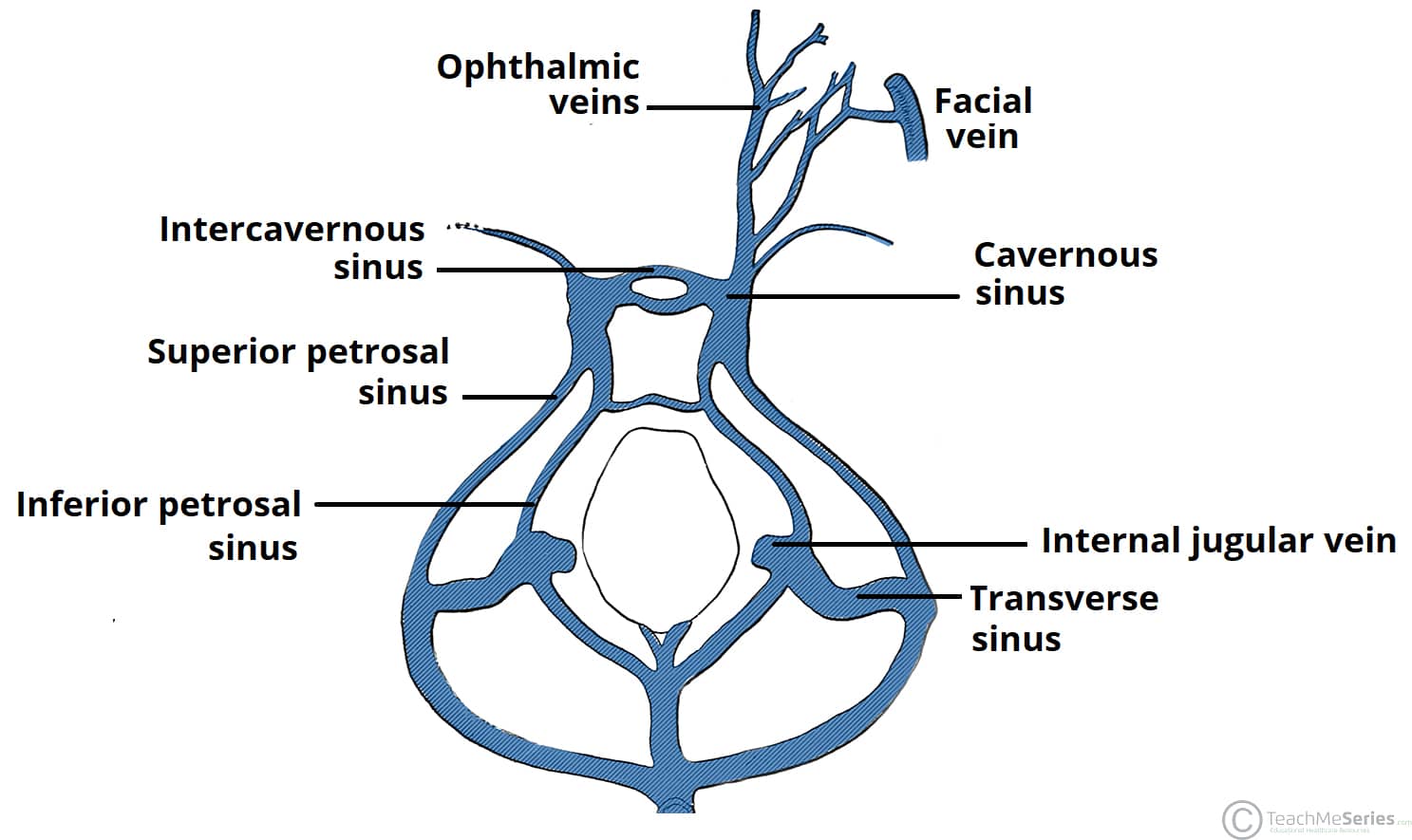



The Cavernous Sinus Contents Borders Thrombosis Teachmeanatomy




Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Emcrit Project




Pin On Sinuses
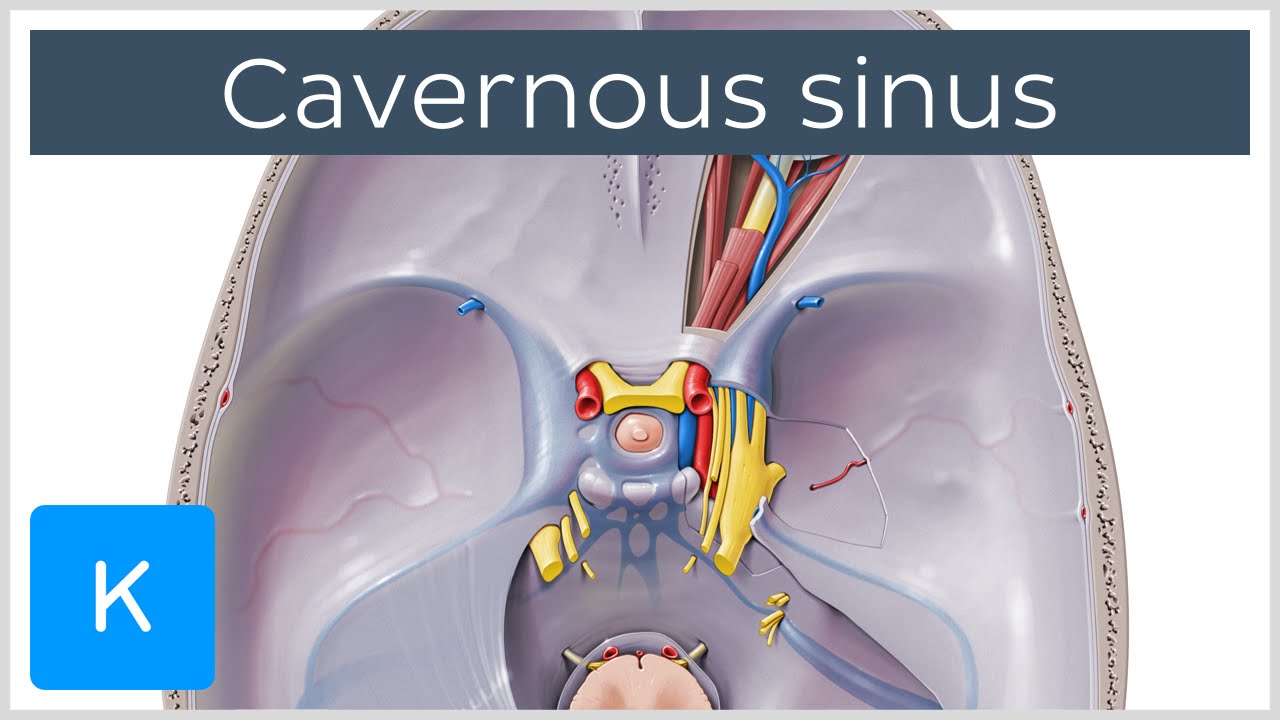



Cavernous Sinus Location Drainage Function Human Anatomy Kenhub Youtube
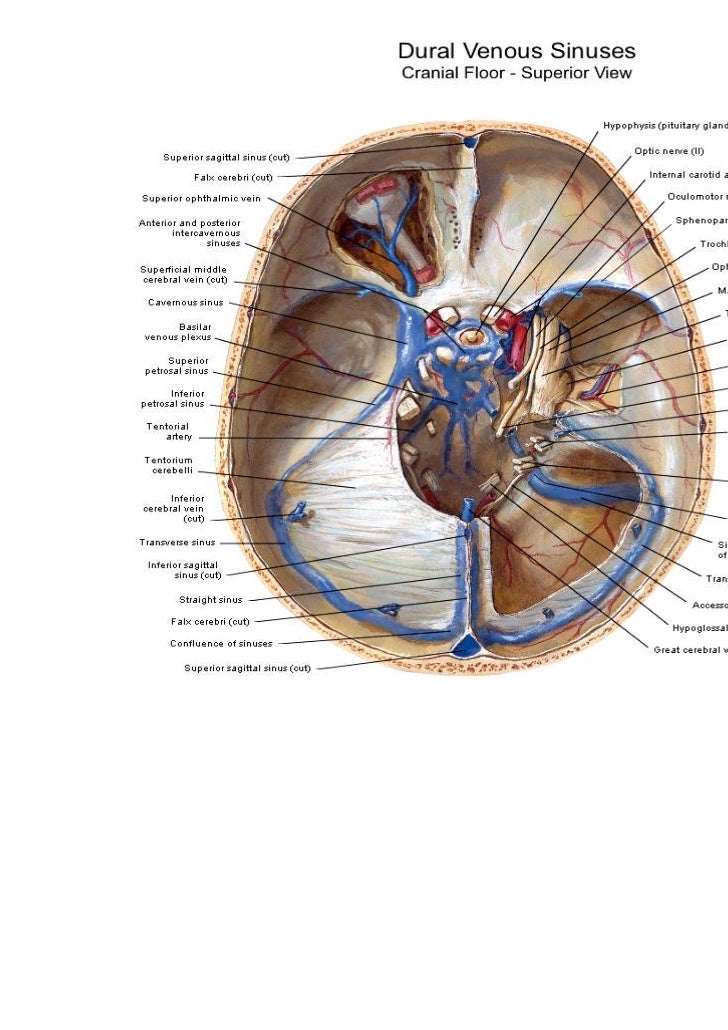



Cavernous Sinus Anatomy




Cavernous Sinus Syndrome Eyewiki




Inferior Cerebral Veins An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Anatomy Of The Cavernous Sinus And Surrounding Structures Relation Download Scientific Diagram




Chapter Solutions Human Anatomy 8th Edition Chegg Com



Dural Venous Sinuses Neurology Medbullets Step 1
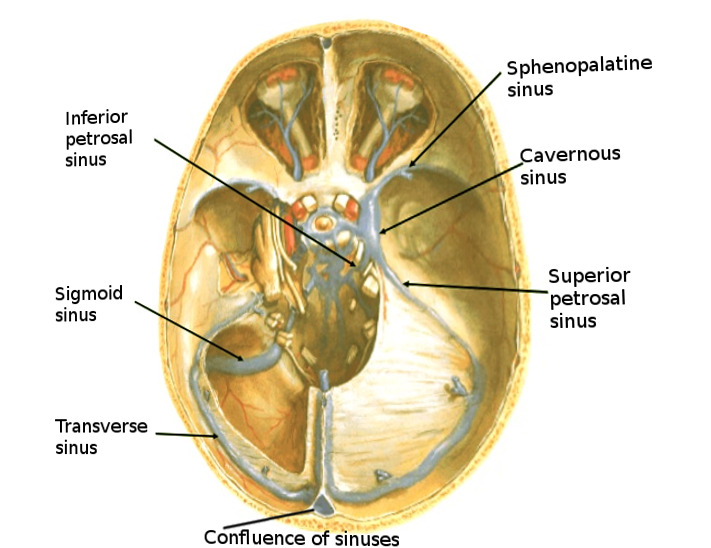



Figure Brain Sinuses Image Courtesy S Bhimji Md Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf
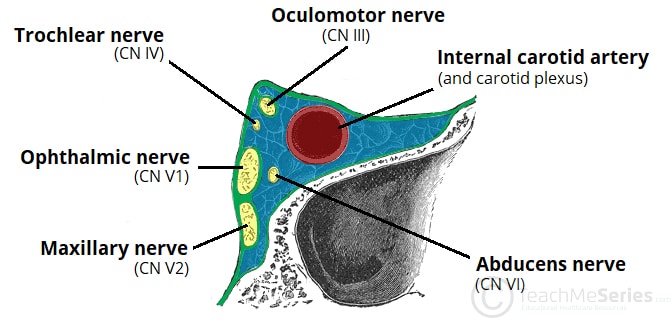



The Cavernous Sinus Contents Borders Thrombosis Teachmeanatomy




Inferior Sagittal Sinus Ppt Video Online Download
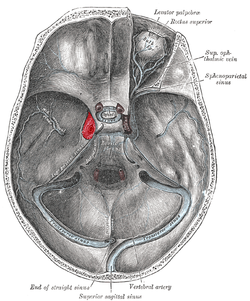



Cavernous Sinus Wikipedia




Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis Linking A Swollen Red Eye And Headache The Lancet




Cavernous Sinus Region



Q Tbn And9gcrf1r8ogr0cp0oo znfe9nz8qwplldxkggncyb03hfu Nwpbj Usqp Cau



Cavernous Sinus Location And Relations Tributaries Connections Thrombosis Anatomyqa




Pin On Neurohirurgija




Anatomy Of The Dural Venous Sinuses Cavernous Sinus Dr Yusuf Youtube




Pin On Anatomy
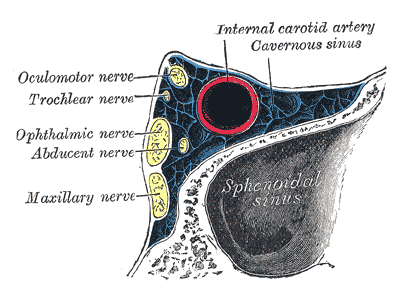



Cavernous Sinus Anatomy And Clinical Relevance Lecturio



1




The Cavernous Sinus Sciencedirect
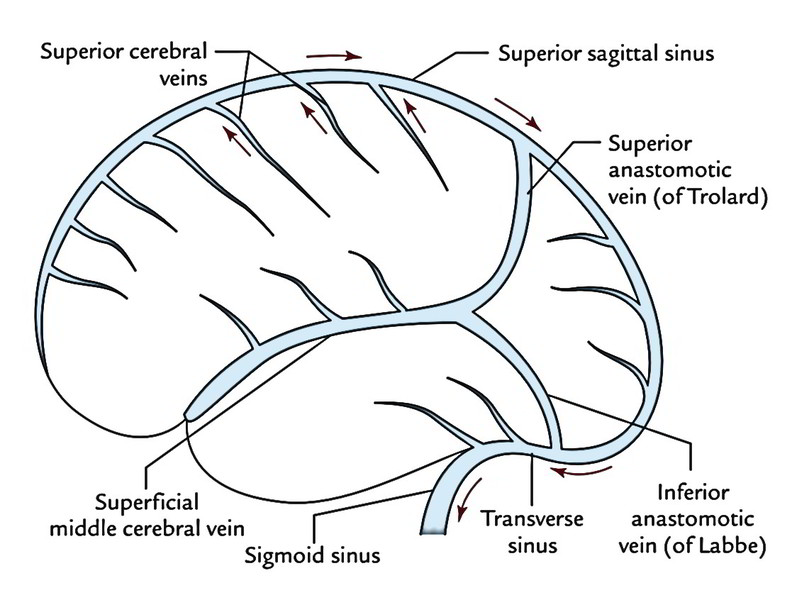



Easy Notes On Venous Drainage Of The Brain Learn In Just 3 Mins Earth S Lab



Cavernous Sinus Neuroangio Org
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/the-cavernous-sinus/CVRbolxCSB6tcLZ4vsOwA_2zVHdd6VW9AS5j54AkD0kg_Sinus_cavernosus_02.png)



Cavernous Sinus Anatomy Kenhub
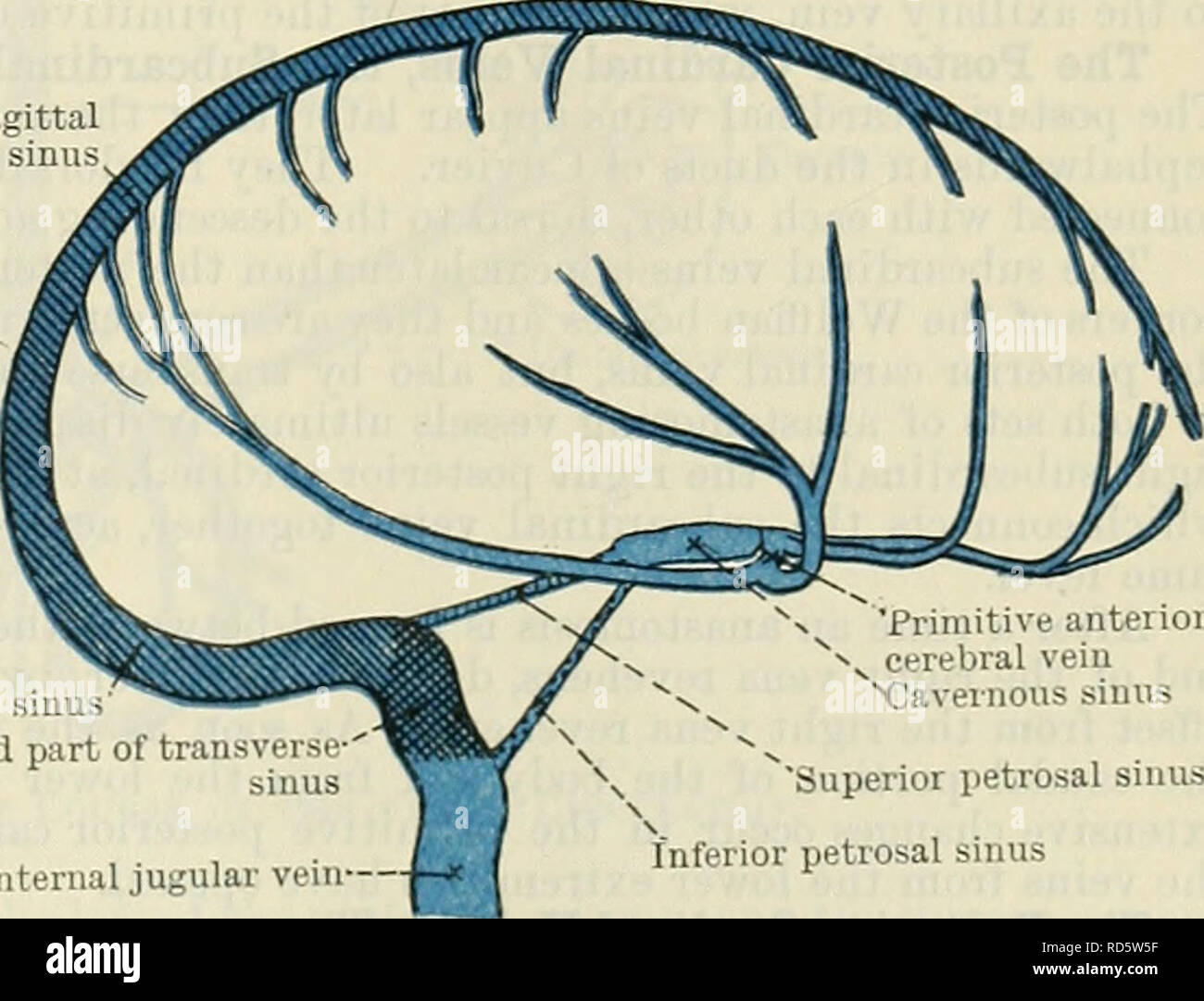



Cunningham S Text Book Of Anatomy Anatomy Ophthalmic Vein Primitive Anterior I Cerebral Vein Semilunar Ganglion Cavernous Sinus Remains Of Lateral Cerebral Vein Primitive Middle Cerebral Vein Otic Vesicle Anterior
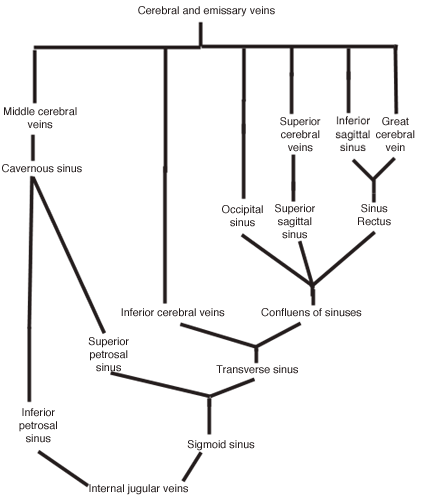



Dissector Answers Neuroanatomy 2




Cerebravascular Anatomy Venous Systempathologies Eyll Yeral The Cerebral




Dural Venous Sinuses An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Anatomy Of The Cavernous Sinus Anatomy Drawing Diagram




Figure Brain Sinuses Image Courtesy S Bhimji Md Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf




Superficial Cerebral Veins An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Epidemiology Diagnosis And Treatment Tidsskrift For Den Norske Legeforening



Cavernous Sinus Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org




38 The Cavernous Sinus Cavernous Applied Anatomy Study Facebook



Cavernous Sinus Neuroangio Org
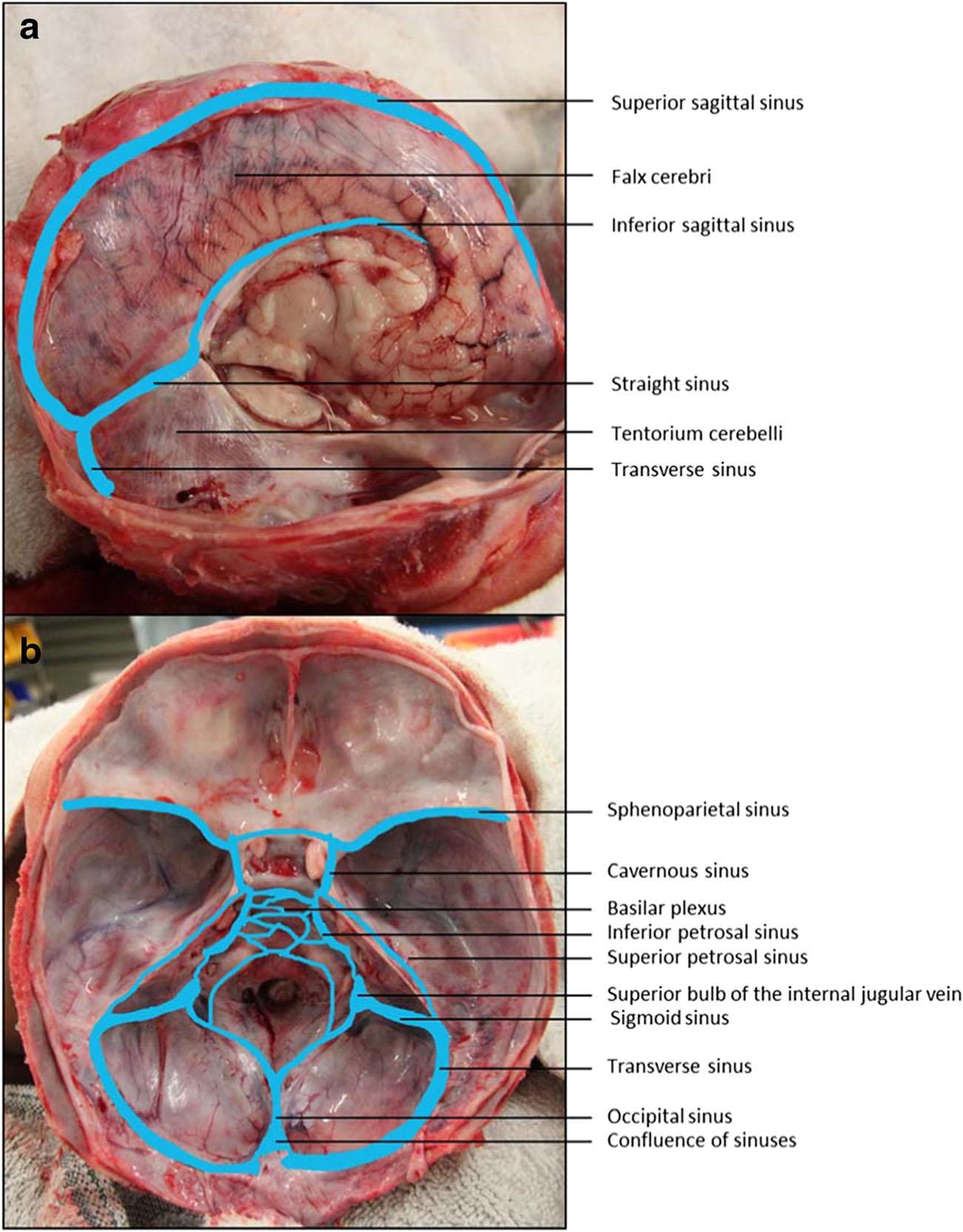



Cavernous Sinus Anatomy And Clinical Relevance Lecturio




Thrombosis Of The Cavernous Sinus Symptoms Causes Treatment Complications




Inferior Cerebral Veins An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
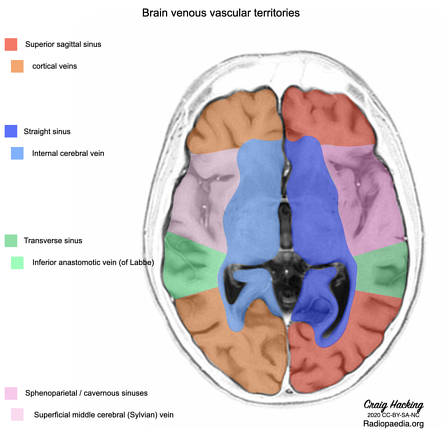



Transverse Sinus Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org



Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcerebral Venous Thrombosis Pearls And Pitfalls Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education
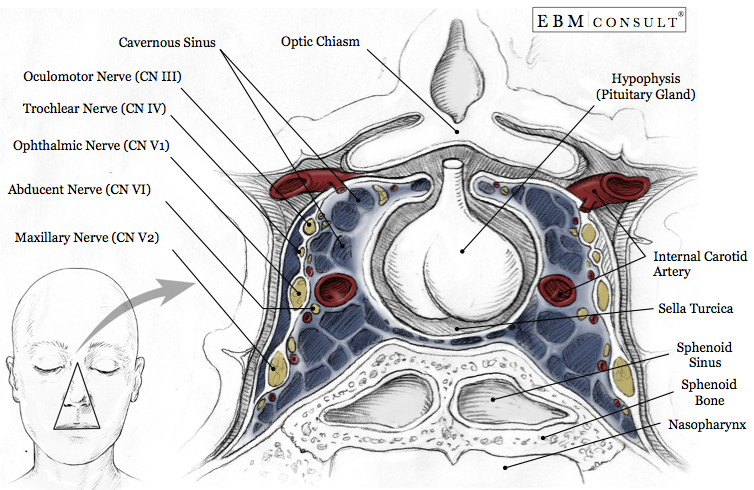



Cavernous Sinus Anatomy
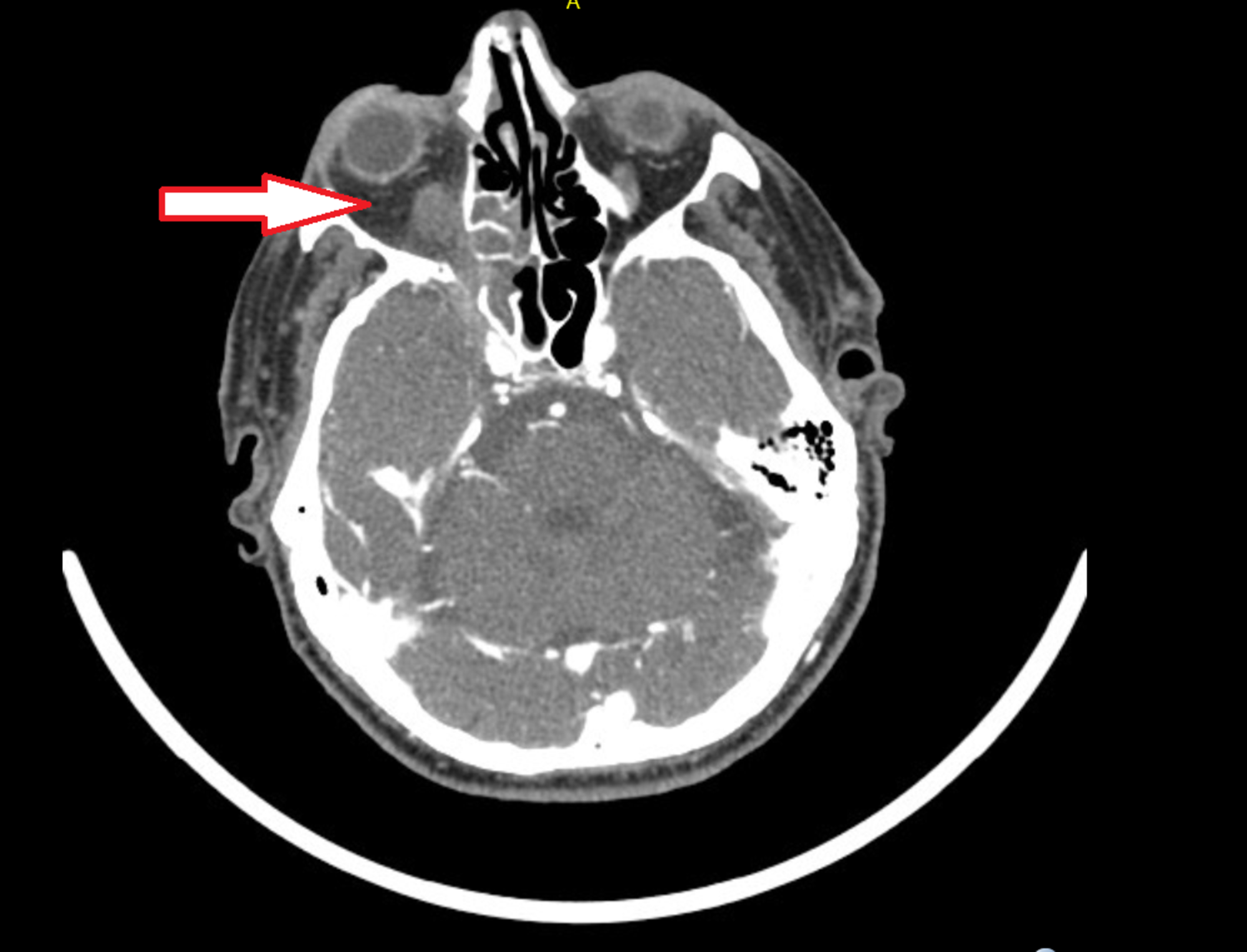



Cureus Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis Due To Chronic Bacterial Sinusitis




Cavernous Sinus Location And Relations Tributaries Connections Thrombosis Anatomyqa




Cavernous Sinus And Proximal Anatomy Neuroanatomy The Neurosurgical Atlas



Cavernous Sinus Neuroangio Org



1




Brain Cavernous Sinus Blood Supply World Of Radiology Facebook



Para Cavernous Sinus Venous Structures Anatomic Variations And Pathologic Conditions Evaluated On Fat Suppressed 3d Fast Gradient Echo Mr Images American Journal Of Neuroradiology



1
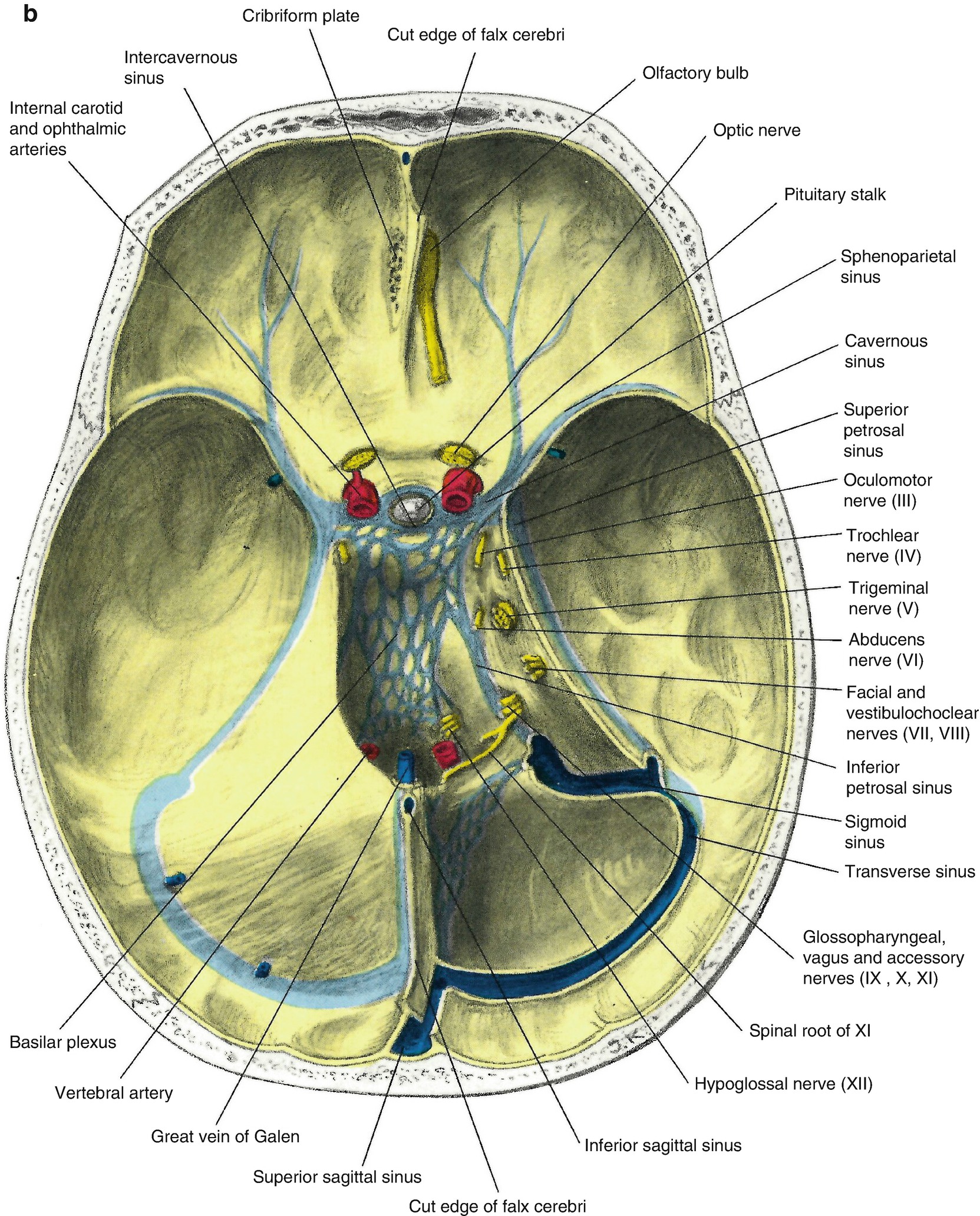



Venous Drainage Of The Brain Springerlink




Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Resus
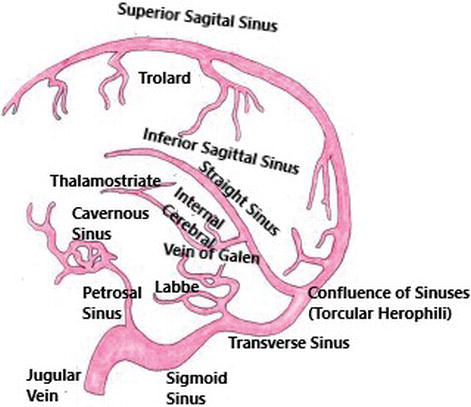



Cerebral Venous Thrombosis A Clinical Overview Intechopen



Imaging Lesions Of The Cavernous Sinus American Journal Of Neuroradiology
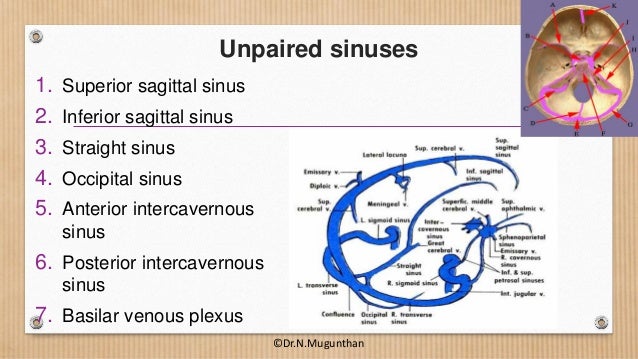



Dural Venous Sinuses Cavernous Sinus Dr N Mugunthan




Septic Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis A Review Survey Of Ophthalmology




Cranial Nerves Within The Cavernous Sinus Ami 18 Meeting
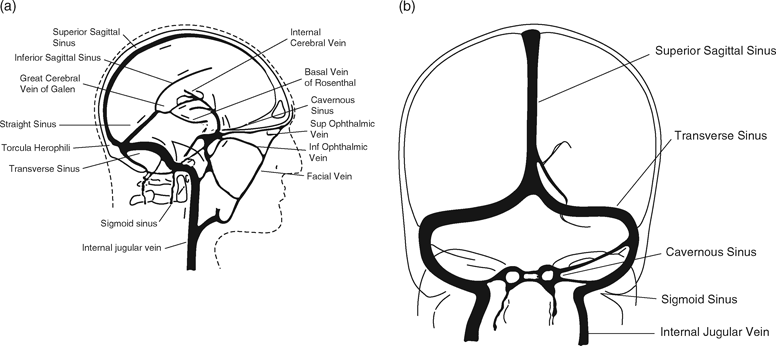



Cerebral Venous Thrombosis And Intracerebral Hemorrhage Chapter 7 Intracerebral Hemorrhage



Ecurriculum Som Vcu Edu Portal Resources 09 Neuro Bloodsupplyduralsin Lecture Pdf




Cavernous Sinus Contents Mnemonic Mnemonic Series 19 Youtube




Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis Wikipedia
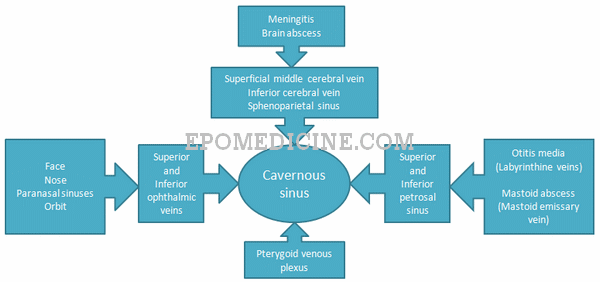



Applied Anatomy Of Cavernous Sinus Epomedicine




Diagram Illustrating The Position Of The Carotid Rete In Artiodactyls Download Scientific Diagram
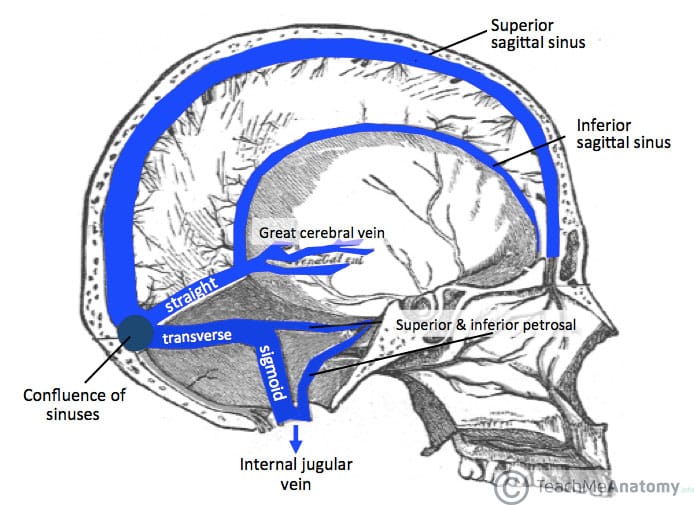



Venous Drainage Of The Cns Cerebrum Teachmeanatomy
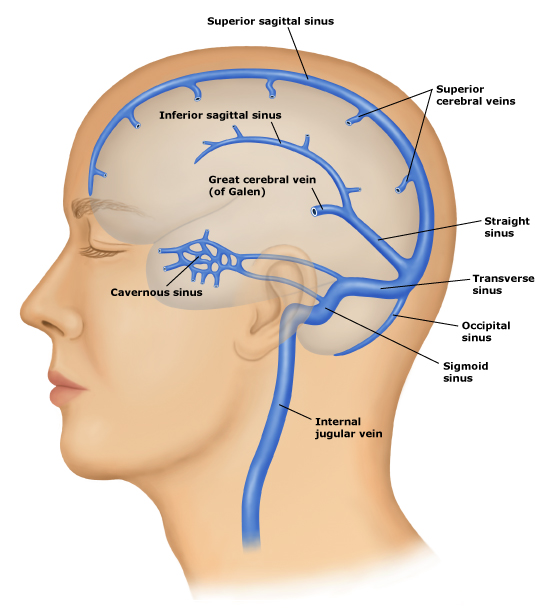



Stroke Medicine For Stroke Physicians And Neurologists




The Cavernous Sinus Sciencedirect
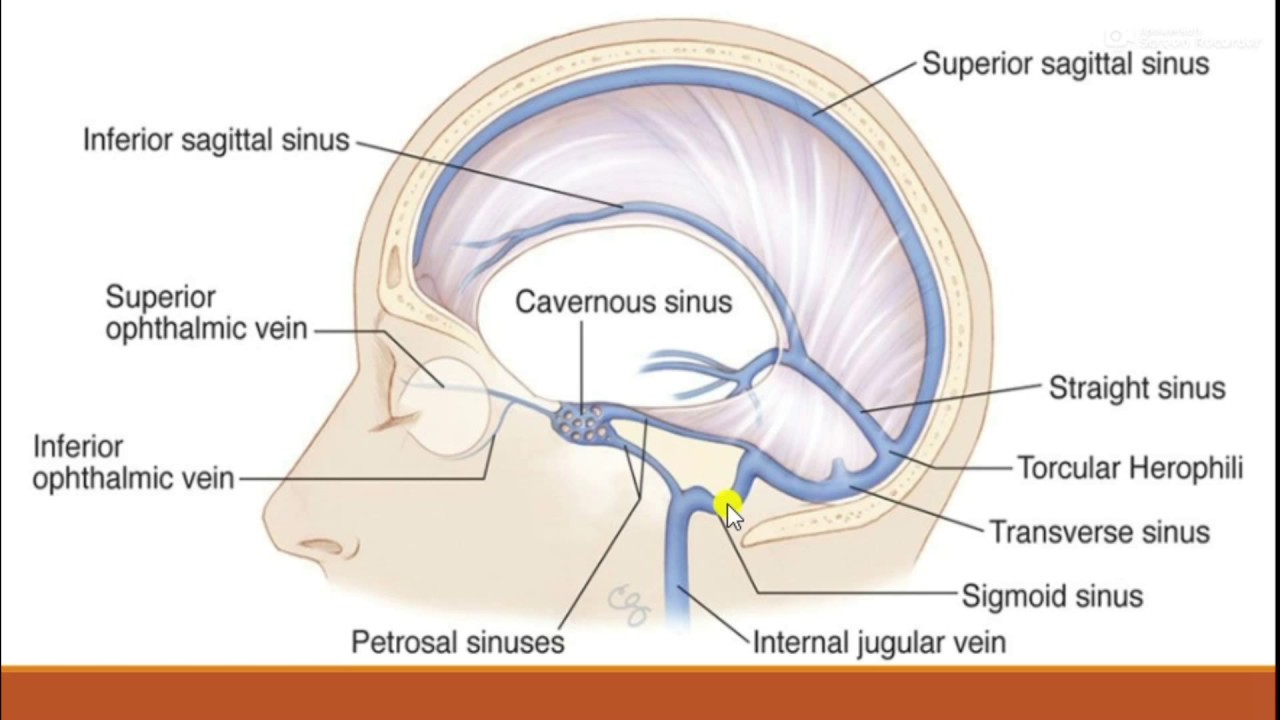



Cavernous Sinus Simply Explained Youtube



Cavernous Sinus Neuroangio Org




Cavernous Sinus
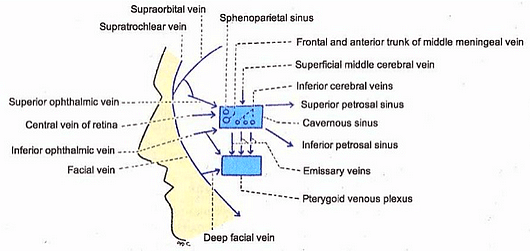



Applied Anatomy Of Cavernous Sinus Epomedicine



Venous Drainage Of The Brain Mednotes




Dangers Of A Tooth Abscess Part 4 Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis




Pin On Amenorreah



Brain Anatomy And Images Brain




Imaging Spectrum Of Cavernous Sinus Lesions With Histopathologic Correlation Radiographics
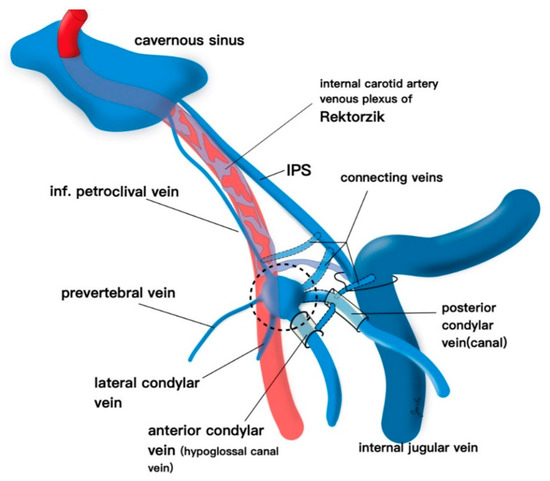



Brain Sciences Free Full Text Endovascular Approaches To The Cavernous Sinus In The Setting Of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Html


コメント
コメントを投稿